Single-mode vs Multimode Fiber: How to Choose Based on Scenarios?
In the field of fiber optic communications, single-mode fiber (SMF) and multimode fiber (MMF) are the two most widely used transmission media. Each has distinct advantages and suits different applications. When deploying networks, how should enterprises or operators choose? This article will guide you through four key dimensions—core differences, performance comparison, application scenarios, and cost analysis—to help you make the optimal decision.
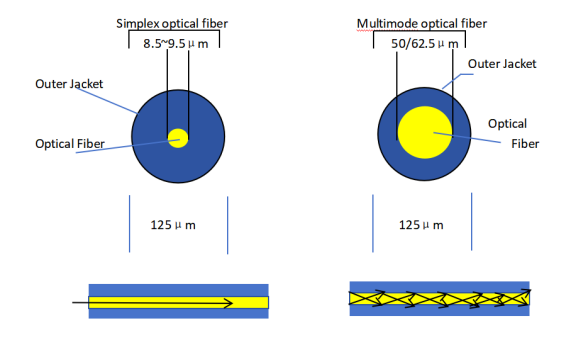
1. Core Differences: Single-mode vs Multimode Fiber
|
Comparison Factor |
Single-mode Fiber (SMF) |
Multimode Fiber (MMF) |
| Core Diameter |
8–10 μm (extremely thin) |
50 μm or 62.5 μm (thicker) |
| Light Source |
Laser (LD) |
LED or VCSEL (Vertical-Cavity Surface-Emitting Laser) |
| Transmission Mode |
Single mode (no modal dispersion) |
Multiple modes (subject to modal dispersion) |
| Typical Wavelengths |
1310 nm / 1550 nm |
850 nm / 1300 nm |
| Bandwidth Capacity |
Ultra-high (Tbps-level; supports 400G/800G) |
High (10G–100G; OM5 supports shortwave WDM) |
| Transmission Distance |
Up to 100+ km (without repeaters) |
Typically <2 km (OM5 up to 500 m @ 100G) |
| Loss |
0.2–0.4 dB/km (low loss) |
2–3 dB/km (higher loss) |
| Bend Resistance |
Poor (requires large bend radius) |
Better (suitable for dense cabling environments) |
| Splicing/Termination |
High precision required |
Forgiving (larger tolerance, easier installation) |
| Typical Applications |
Telecom backbone, 5G fronthaul, FTTH, submarine cables |
Data centers, enterprise LANs, security surveillance |
| Cost |
Lower fiber cost, higher module cost |
Higher fiber cost, lower module cost |
Key Distinction:
- SMF’s ultra-thin core eliminates modal dispersion, making it ideal for long-distance, high-bandwidth applications (e.g., telecom backbones).
- MMF’s thicker core allows multiple light paths, reducing costs for short-range deployments (e.g., data centers).
2. Performance Comparison: Bandwidth, Distance, and Loss
(1) Bandwidth Capability
- SMF: Theoretical bandwidth up to Tbps (e.g., 400G/800G), future-proof for upgrades.
- MMF: Supports 10G–100G (OM3/OM4/OM5), cost-effective for short distances.
(2) Transmission Distance
|
Speed |
SMF |
MMF OM4 |
MMF OM5 |
|
1G |
100+ km/328+ft |
1 km/3280ft |
1 km/3280ft |
|
10G |
80 km/262400ft |
300 m/984ft |
400 m/1312ft |
|
40G |
40 km/131200ft |
100 m/328ft |
150 m/492ft |
|
100G |
10~40 km |
100 m/328ft |
150 m/492ft |
Conclusion:
- Long distances (>2 km): Use SMF (e.g., metropolitan networks, submarine cables).
- Short distances (<500 m): MMF (OM4/OM5) is more economical.
(3) Loss and Interference Resistance
- SMF: Low loss (0.2–0.4 dB/km), ideal for long-haul but requires precise splicing.
- MMF: Higher loss (2–3 dB/km) but better bend resistance (e.g., data center deployments).
3. Scenario-Based Selection Guide
✅ Choose SMF if:
✔Telecom Backbone Network (long-distance, high-bandwidth requirements
✔ 5G Fronthaul/Midhaul (low latency, high reliability)
✔ FTTH (Fiber to the Home) (future upgrade requirements)
✔ Inter-Data Center Interconnection (scenarios over 10km)
✅ Choose MMF if:
✔Short-range LANs (e.g., data centers, enterprise networks)
✔Cost-sensitive deployments
✔Harsh environments (e.g., industrial automation requiring flexible cabling)

Special Case:
- OM5 (WBMMF): Supports shortwave WDM, enabling 425G over a single fiber. Ideal for future-proof 100G/400G data centers.
4. Cost Analysis: CAPEX vs. OPEX
|
Cost Factor |
SMF |
MMF |
| Fiber Cost | Lower | Higher (OM4/OM5) |
| Module Cost | Higher (laser-based) | Lower (VCSEL-based) |
| Installation | Complex (precision alignment) | Simpler (greater tolerance) |
| Long-Term Scalability | Superior (supports Tbps) | Limited (may require upgrades beyond 100G) |
Decision Summary
- Budget-friendly + short-range: MMF (OM4/OM5).
- Future expansion + long-haul: SMF (costly upfront but economical long-term).
5. Final Recommendation
Select SMF if:
- Need >2 km reach
- Plan to upgrade to 100G+
- Require telecom-grade reliability
Select MMF if:
- Deploying within <500 m (e.g., data centers)
- Prioritizing low-cost installation
- Operating in complex enviro
 nments
nments
Hybrid Approach: Combine SMF backbones with MMF access networks for balanced cost/performance.
Need help with your fiber-optic deployment? Contact our technical team or visit Raisefiber.com for free consulting + customized solutions!
SEO Keywords: Single-mode vs Multimode Fiber, Fiber Selection Guide, OM4 vs OM5, Data Center Fiber, Long-Haul Communications
Post time: Jul-23-2025

